Currently, about 94% of companies worldwide use AI in at least one business operation.
This is a significant jump from 2017, when just 20% of the companies were experimenting with AI. Such a huge surge highlights how quickly businesses are adopting AI and moving beyond early experiments to real-world results.
In fact, in 2024, private companies around the globe invested over $252.3 billion into AI. And not only into hiring, customer service, or cybersecurity, these companies are implementing AI into every other business function.
In this report, you will have clear insights into how many companies use AI and how they are adopting AI to boost revenue and business performance.
Top Picks From This Report
- 94% of companies across the world use AI in at least one operation of their business. That accounts to 417.4 million companies.
- 79% of the companies make use of generative AI in their everyday business functions.
- The AI market size is expected to reach $1.89 trillion in 2030.
- India has the highest AI adoption rates, with around 59% of the companies actively using AI in their operations.
- All of Fortune 500 companies utilise AI for their businesses.
- 58% companies with revenue of $5 billion and more are fully scaling AI to automate operations.
- In 2024, global private investment by companies into AI reached $252.3 billion.
How many companies use AI globally?
As of 2026, 94% of companies use AI in at least one business function worldwide. With around 444 million companies operating globally, this means over 417.4 million businesses are already using AI or actively exploring it to improve how they work, make decisions, and run their operations.
This represents a 6% jump from 2025, when approximately 88% of companies were using AI.
In 2017, only about 20% of companies had begun using AI, mainly through pilots rather than full-scale adoption. The real acceleration began after 2020, when AI became more accessible to both the public and large companies.
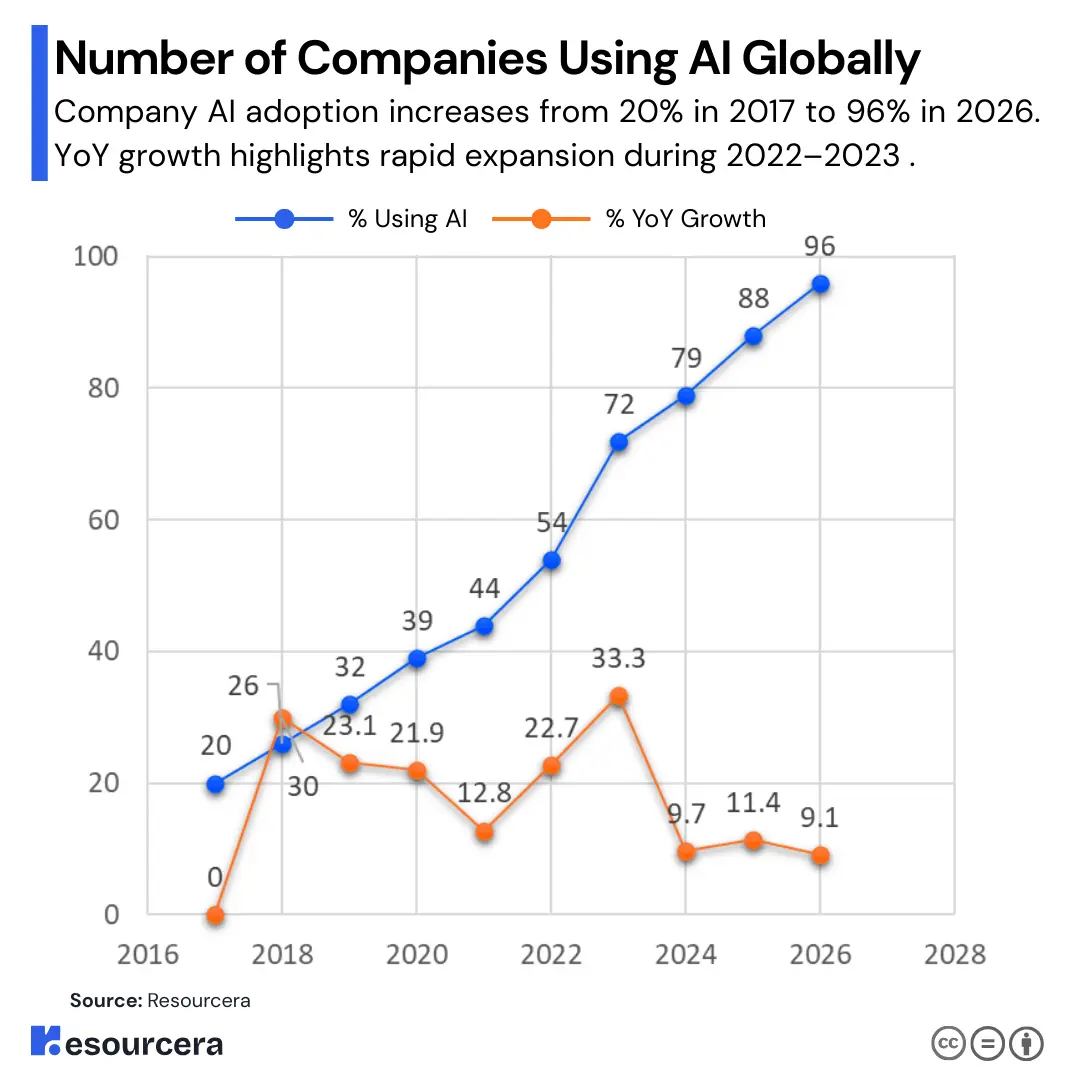
Here is a breakdown of AI adoption by companies worldwide over the years:
| Year | % of companies using AI in at least 1 function |
|---|---|
| 2017 | 20% |
| 2018 | 26% |
| 2019 | 32% |
| 2020 | 39% |
| 2021 | 44% |
| 2022 | 54% |
| 2023 | 72% |
| 2024 | 79% |
| 2025 | 88% |
| 2026 | 96% |
Generative AI is also on the rise. Currently, 79% of businesses use generative AI in their daily business tasks.
This is a massive increase, showing that companies are not just using basic machine learning for tasks like data analysis or automation, but are also leveraging AI to create new content, documents, marketing materials, code, and more.
How Many Fortune 500 Companies Are Using Ai?
As of 2026, 100% of Fortune 500 companies use artificial intelligence in their business operations. This includes direct AI-powered products, internal automation, analytics, cybersecurity, customer experience, finance, supply chain, and decision-making systems.
This conclusion is based on Resourcera’s manual review of official company blogs, press releases, earnings reports, and credible news coverage for every Fortune 500 company, along with supporting data from large-scale enterprise technology providers and executive surveys.
We wanted to know the state of AI adoption in these Fortune 500 companies, We dig deep and found a official Fortune study where 300 senior leaders at Fortune 500 companies, including C-suite executives (CEO, COO, CFO, CHRO, CRO) as well as EVPs, SVPs, VPs, and directors were surveyed. Below are the findings:
- 70% of Fortune 500 executives say their companies have an AI risk committee.
- 67% report active progress on AI infrastructure.
- 41% have a dedicated AI governance team.
- Only 14% say their company is fully ready for AI deployment at scale.
We did not end our quest there. We went deeper and found this interesting data from Microsoft’s official blog. Microsoft itself is a fortune 500 company and one of the biggest investors in AI. Here is what we found:
- Nearly 90% of Fortune 500 companies use Microsoft 365 Copilot in daily workflows.
- 80% of the Fortune 500 use Microsoft Foundry for building or deploying AI models.
- 90% of Fortune 100 companies use GitHub Copilot for AI-assisted software development.
- 90% of Fortune 500 companies use Copilot Studio to build internal AI tools and automation.
Source: Internal Data, Fortune, Microsoft.
At What Stages Companies are Using AI
Though all these companies use AI, not all of them are at the same stage. About 32% of organizations are still experimenting with AI functions, while 30% of them are piloting AI.
Surprisingly, only 7% of the companies have fully scaled AI into their business functions.
Here is how these companies are using AI in 2026:
| Phase of AI use among organizations | % of organizations |
|---|---|
| Fully scaled | 7% |
| Scaling | 31% |
| Piloting | 30% |
| Experimenting | 32% |
While the adoption of AI in a single function is impressive, the data shows that companies are increasingly using AI across two, three, or even more areas of their business.
70% of organizations now report using AI in at least two functions, 51% in three or more, and 33% in four or more. Even 20% of companies are achieving adoption in five or more functions.
Despite this progress, most organizations are still in the pilot phase. This means that many are trying AI out in select areas rather than rolling it out everywhere at once.
More than two-thirds of respondents now say their company uses AI in more than one function, and about half use AI in three or more functions.
Here is a quick insight into companies using AI in their different business functions in 2026:
| 1 or more functions | 94% |
| 2 or more functions | 70% |
| 3 or more functions | 51% |
| 4 or more functions | 33% |
| 5 or more functions | 20% |
Businesses tend to start with pilot projects, seeing how AI helps with tasks like customer service, inventory management, marketing, or HR. If those projects deliver good results, companies often decide to expand into other departments.
(Source: McKinsey Report, AI Statistics)
Breakdown of Companies Using AI by Company Revenue
Not all companies are approaching AI in the same way, and company size makes a big difference.
Big businesses are much more likely to scale AI across their organizations, while smaller companies are often still in the early stages, experimenting or running pilots.
To put that into the numbers, smaller companies with less than $100 million in revenue, are mostly experimenting with AI across their business functions. Only 5% of them have fully scaled AI usage into their operations.
Companies with $100 million to $999 million are mostly piloting and scaling AI, but the percentage of fully scaled adoption is still low.
Whereas, companies having $5 billion or more are leading the way, with 19% having fully scaled AI across all business functions and 39% actively scaling up from pilots.
Here is the use of AI based on the revenue:
| Company Revenue | Not Using AI | Experimenting | Piloting | Scaling | Fully Scaled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <$100 million | 9% | 39% | 25% | 22% | 5% |
| $100m – $499m | 4% | 33% | 37% | 23% | 4% |
| $500m – $999m | 5% | 31% | 32% | 29% | 3% |
| $1b – $4.9b | 1% | 31% | 32% | 33% | 3% |
| $5 billion or more | 1% | 10% | 31% | 39% | 19% |
(Source: McKinsey)
Investment by companies into AI
In 2024, the global private AI investment reached over $252.3 billion.
Similarly, the investment for generative AI reached around $34 billion, up 12.1% from 2023.
Companies are putting real money into AI, and the level of investment usually depends on how big the company is. In 2024, most organizations, especially the larger ones, are making responsible AI (RAI) a budget priority.
RAI investments include things like developing secure systems and making sure everything follows good standards and safety rules.
Smaller companies (income less than $100M) keep it modest: 68% invest between $1–5M in AI, and only 6% go as high as $10–25M.
Here’s how investment looks based on company size:
| Company Annual Revenue | $1–5M | $5–10M | $10–25M | $25–50M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Less than $100M | 68% | 25% | 6% | 1% |
| $100M–$1B | 48% | 30% | 15% | 7% |
| $1B–$10B | 40% | 32% | 18% | 10% |
| $10B–$30B | 24% | 30% | 27% | 19% |
| Over $30B | 25% | 29% | 21% | 25% |
(Source: Stanford Report)
AI Adoption in Companies by Industry
AI in healthcare, financial services, telecommunications, and the government sector industries are leading in adoption rate.
Nearly half of all companies in financial services and government (49%) have fully integrated AI into their business operations.
For telecom, 37% are actively using AI, and 45% are exploring its use. In industrial companies, 42% are using AI, and 46% are in the testing phase.
This suggests that companies handling lots of customer data or complex operations know AI can offer significant advantages, but many are still figuring out the best way to apply it.
The data below suggests how different industries are adopting AI in their operations:
| Industry | Actively Using AI (%) | Exploring AI (%) | Not Using AI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | 49% | 33% | 15% |
| Industrial | 42% | 46% | 11% |
| Healthcare | 25% | 47% | 20% |
| Telecommunications | 37% | 45% | 16% |
| Government | 18% | 49% | 24% |
| Energy, Environment, Utilities | 23% | 51% | 21% |
| Automotive | 37% | 44% | 13% |
| Retail | 31% | 42% | 21% |
| Travel & Transportation | 31% | 53% | 13% |
| Global Enterprise (All industries) | 42% | 40% | 15% |
(Source: IBM)
Business Functions Using AI
Customer Service is the function with the most popular use of AI. Infact, over half of the companies (56%) use AI for their Customer Service tasks to help customers faster and more efficiently.
Security and Fraud comes next with 51% of the companies using AI for cybersecurity and fraud detection.
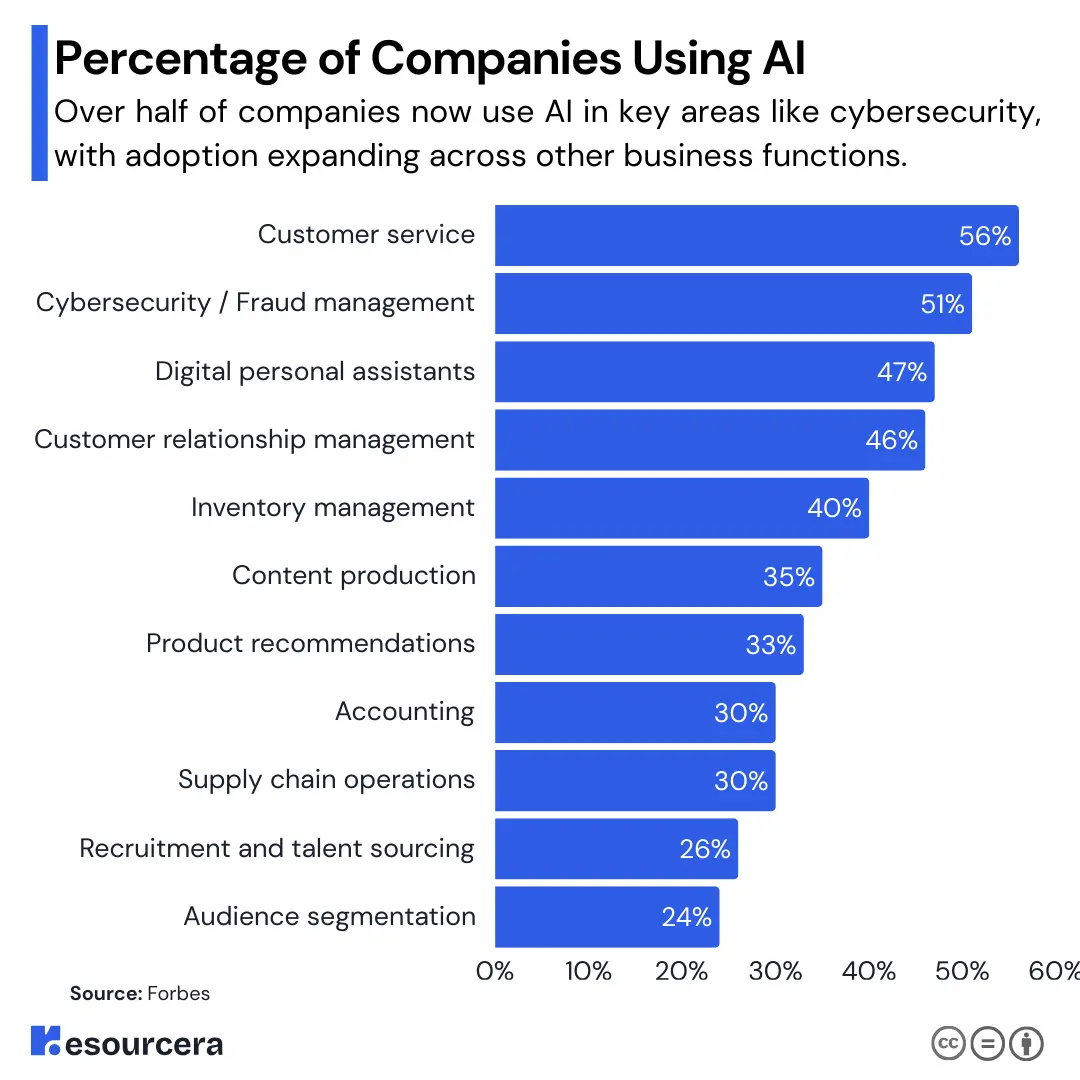
Let’s look at where AI has gained the most ground:
| AI Application Area | Percentage of Companies Using AI |
|---|---|
| Customer service | 56% |
| Cybersecurity / Fraud management | 51% |
| Digital personal assistants | 47% |
| Customer relationship management | 46% |
| Inventory management | 40% |
| Content production | 35% |
| Product recommendations | 33% |
| Accounting | 30% |
| Supply chain operations | 30% |
| Recruitment and talent sourcing | 26% |
| Audience segmentation | 24% |
(Source: Forbes)
How Companies Are Adopting AI by Region
Asia leads the way in company AI adoption, with India, the UAE, Singapore, and China among the top.
As of 2026, India stands out as the leader in AI adoption, with 59% of companies actively using AI in their day-to-day business. This high rate puts India in the top spot globally for AI deployment in companies.
Next comes the United Arab Emirates, where 58% of businesses have brought AI into their operations. Singapore is also among the top adopters, at 53%.
These countries have made strong investments in technology and are eager to stay ahead in business efficiency and innovation.
In contrast, the United States, often thought of as a tech leader, shows one of the lowest adoption rates, with only 33% of companies actively using AI. This is surprisingly low compared to other countries and points to regional differences in how quickly businesses are embracing AI.
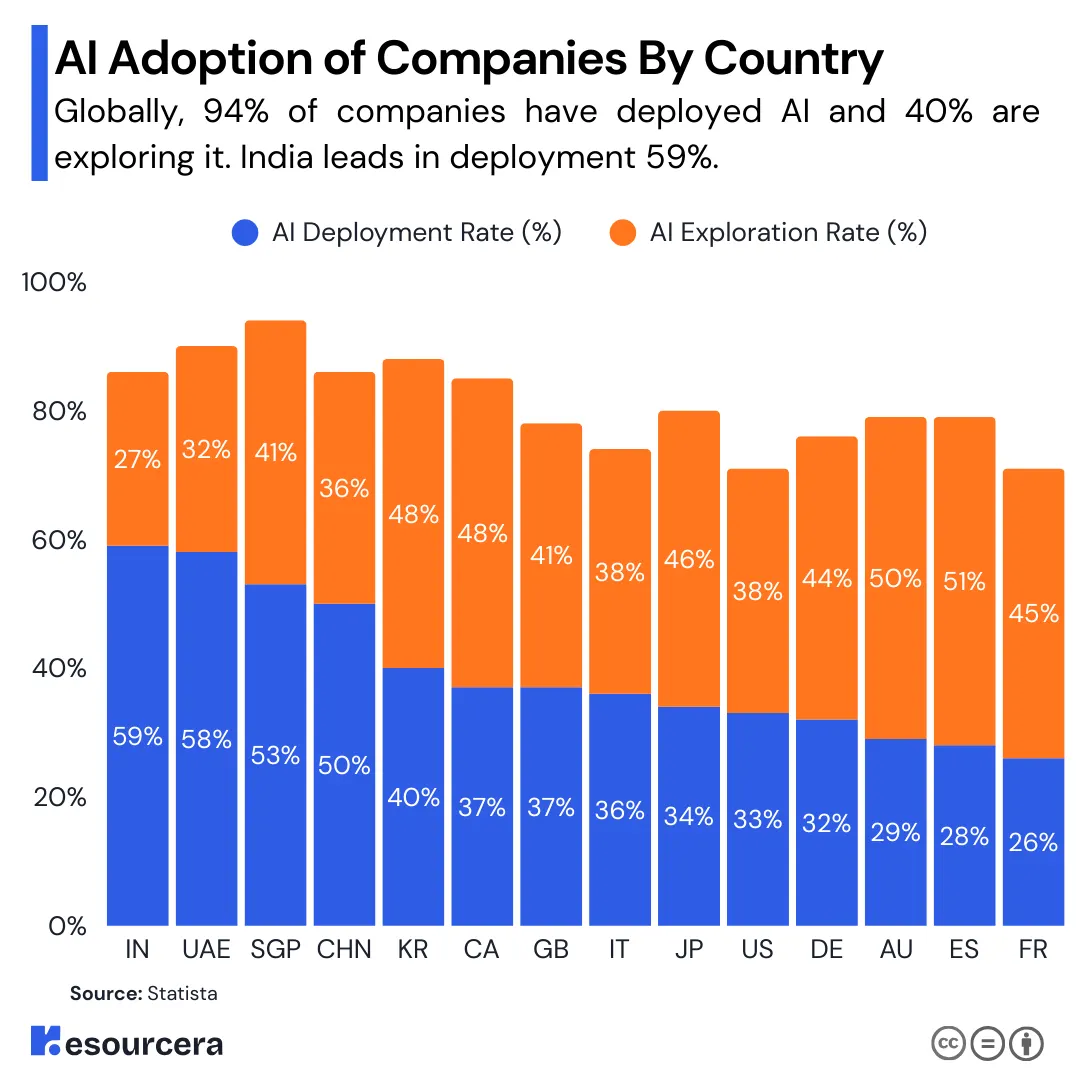
For a clearer look, here’s a table showing the AI adoption rates of companies by country:
| Country/Region | AI Deployment Rate (%) | AI Exploration Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| India | 59% | 27% |
| United Arab Emirates | 58% | 32% |
| Singapore | 53% | 41% |
| China | 50% | 36% |
| Latin America | 47% | 34% |
| South Korea | 40% | 48% |
| Canada | 37% | 48% |
| United Kingdom | 37% | 41% |
| Italy | 36% | 38% |
| Japan | 34% | 46% |
| United States | 33% | 38% |
| Germany | 32% | 44% |
| Australia | 29% | 50% |
| Spain | 28% | 51% |
| France | 26% | 45% |
(Source: IBM, Statista)
Company Benefits and ROI Using AI
According to a recent global survey, companies mainly report that AI helps the most with innovation, employee and customer satisfaction, and staying ahead of the competition.
Looking at the numbers, a huge 64% of organizations say AI has helped them become more innovative in the past year. This is the top-cited benefit, with nearly two out of three companies seeing their ability to generate and launch new ideas improve.
Alongside this, 45% of businesses also reported better customer satisfaction, likely due to faster service, better recommendations, or smarter support teams.
Thirty-eight percent of businesses saved costs, while 36% saw a direct impact on profits.
Organic revenue growth, which is growth coming from existing business activities rather than new investments, improved for 33% of companies.
Here’s a quick look at how companies are benefiting from using AI:
| Area of Improvement | % of Organizations Reporting Benefit |
|---|---|
| Innovation | 64% |
| Employee Satisfaction | 45% |
| Customer Satisfaction | 45% |
| Competitive Differentiation | 45% |
| Cost | 38% |
| Profitability | 36% |
| Organic Revenue Growth | 33% |
| Attraction/Retention of Talent | 31% |
| Change in Market Share | 25% |
Revenue increase within business units from AI use, by function
Now what about money in and money out?
If we look at revenue, marketing, and sales clearly get the biggest boost from AI, with 67% of businesses in these areas seeing revenue increases, and 10% reporting jumps of more than 10%.
Strategy, corporate finance, and product or service development are close behind, with about two-thirds of companies in these functions also seeing an uptick in revenue, again, 10-12% report gains over 10%.
Even more operational functions like supply chain management and IT saw notable results, though the impact was slightly smaller.
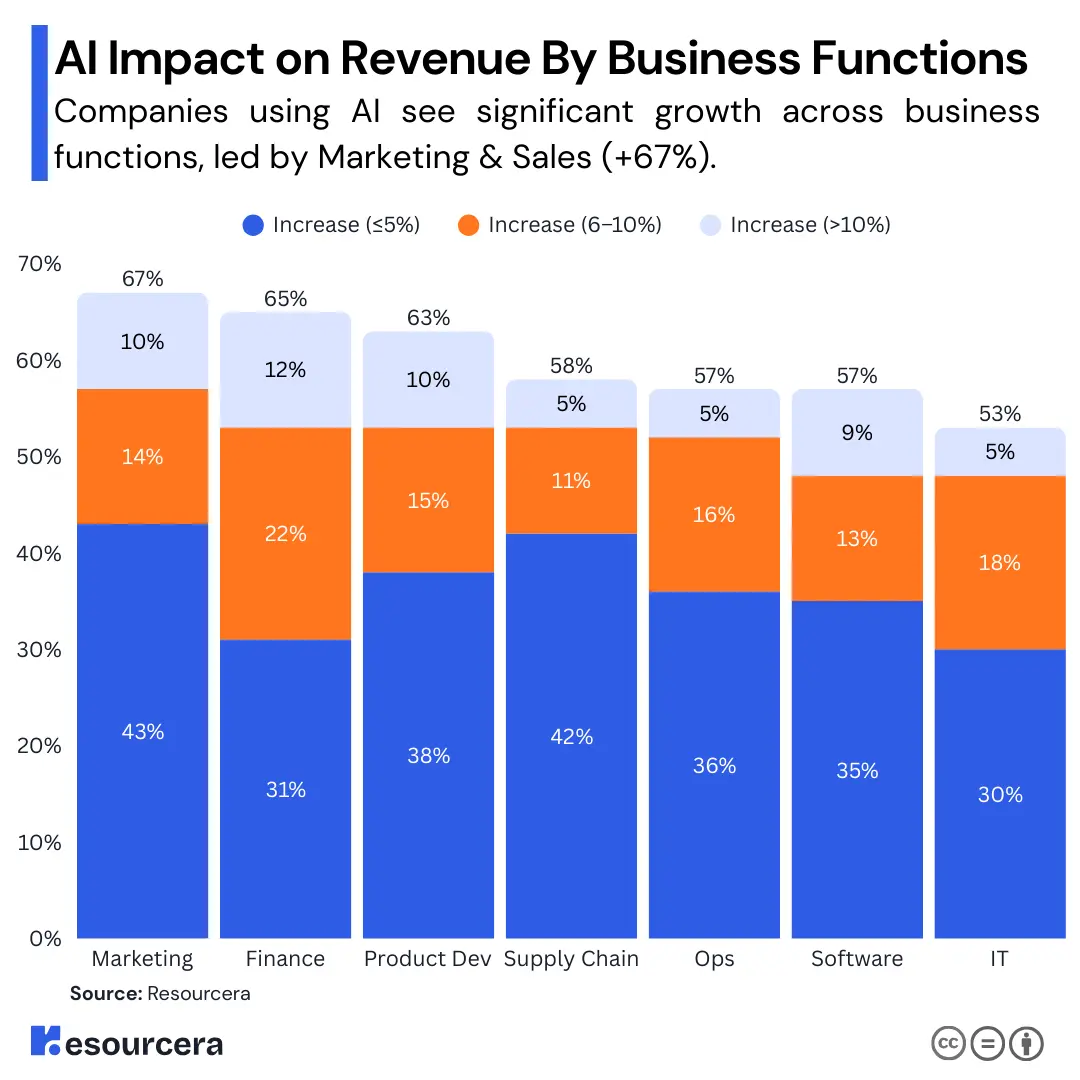
| Business Function | Total % increase in business function among companies using AI |
|---|---|
| Marketing and Sales | 67% |
| Strategy and Corporate Finance | 65% |
| Product/Service Development | 62% |
| Supply Chain & Inventory Management | 59% |
| Service Operations | 57% |
| Software Engineering | 57% |
| IT | 52% |
Cost Reduction from AI use by function
Now, when it comes to cutting costs, which is equally important, AI is making a real mark in software engineering, manufacturing, and IT departments.
56% of software engineering teams and 56% of manufacturing groups saw their costs go down. In IT, 54% reported reduced spending.
Below is the data suggesting how companies have benefited by cutting the costs:
| Function or Department | Total % decrease in cost within business functions by using AI |
|---|---|
| Software engineering | 56% |
| Manufacturing | 56% |
| IT | 54% |
| Strategy and corporate finance | 53% |
| Service operations | 51% |
| Human resources | 51% |
| Supply chain and inventory management | 49% |
| Marketing and sales | 49% |
| Product or service development | 47% |
| Risk, legal, and compliance | 45% |
| Knowledge management | 44% |
Future Outlook of Companies Using AI
The role of artificial intelligence in business is only expected to grow stronger in the coming years.
As businesses discover what AI can do, there’s also a rising demand for employees with the right skills. In fact, 66% of business owners and executives say they have hired new staff specifically to work with AI or to help use it better in daily work.
Further, one of the most noteworthy findings is the impact AI is having on daily work routines. AI is helping employees save an average of 2.5 hours every single day.
Currently, 28% of business leaders say they’ve tapped into AI to reduce their company’s expenses. These savings might come from automating daily processes, cutting down on manual labor, or streamlining operations to avoid costly mistakes.
Impact Of AI On Jobs and Employment
AI is changing the job market, and companies, especially larger ones, are hiring people for more AI-related roles than ever before. The demand is highest for technical experts, but new opportunities are showing up in other business roles too.
Software engineers and data experts are the most in-demand AI roles, especially in larger companies. 14% of organizations with over $1B revenue have hired data scientists and engineers, compared to 9-10% for smaller companies.
Hiring for AI roles is much more common in large organizations. Smaller companies are catching up, but 36% of large organizations haven’t hired for any AI position in the last year, compared to almost half (48%) for smaller businesses.
Let’s take a look at share of organizations that hired for each position in the past year:
| AI Job Role | Companies >$1B Revenue (%) | Companies <$1B Revenue (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AI data scientists | 30% | 14% |
| Data engineers | 29% | 19% |
| Machine learning engineers | 29% | 14% |
| Software engineers | 29% | 23% |
| AI product owners/managers | 26% | 17% |
| Data architects | 26% | 13% |
| Data visualization specialists | 20% | 10% |
| Design specialists | 18% | 13% |
| AI compliance/legal experts | 16% | 6% |
| Prompt engineers | 14% | 10% |
| Translators | 13% | 5% |
| All other AI specialists | 6% | 4% |
| None of the above | 10% | 35% |
Challenges Faced by Companies in Using AI
As more businesses use AI, they are coming up against a range of challenges, and many are putting effort into managing these risks.
The biggest challenge reported by companies is inaccuracy; 30% of companies have faced this issue during the past year. Inaccuracy in AI can show up as wrong predictions, incorrect reports, or systems not working as planned.
Many firms say they are actively working to fix these issues. According to the latest data, 54% of respondents said their organization is working to mitigate inaccuracy, making it the top concern.
Moreover, 24% of global companies and business owners worry that AI could reduce their search engine visibility.
Companies also report other risks, including cybersecurity and intellectual property security, as well as personal privacy issues.
Here’s how often organizations have experienced different negative consequences, and how many are working to manage each risk:
| AI Risk/Challenge | Experienced at least once (%) | Working to mitigate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccuracy | 30 | 54 |
| Cybersecurity | 10 | 51 |
| Regulatory compliance | 8 | 43 |
| Intellectual property | 8 | 38 |
| Personal privacy | 11 | 38 |
| Unintended AI interaction | 7 | 28 |
| Explainability | 14 | 28 |
| Organiational reputation | 5 | 27 |
| Equity and fairness | 7 | 21 |
| Workforce and labor | 6 | 14 |
| Environmental impact | 3 | 10 |
| National security | 3 | 10 |
| Physical safety | 1 | 8 |
| Political stability | 3 | 5 |
| None of the above | 29 | 3 |
Despite these challenges, companies are becoming more proactive. The top three types of risks being managed right now are inaccuracy (54%), cybersecurity (51%), and intellectual property security (48%). Explainability, fairness, and workforce impact are less commonly tackled but are still on the radar.
Finally, it’s worth noting that 39% of companies didn’t experience any of these challenges in the past year. That means most problems are concentrated in a smaller but significant group of businesses.
Final Thoughts
So, coming to the conclusion, 94% of companies worldwide are now using AI in at least one core function and 79% adopting generative AI.
Adoption spans all industries and company sizes, though large enterprises and sectors like finance are leading the way.
Most organizations start with small pilots, but a growing number are scaling AI into multiple areas.
The consistent year-over-year growth shows AI is no longer just an experiment, it’s a core part of how business is done.
The gap between early adopters and cautious companies is shrinking fast, and those who adapt are seeing real productivity gains and better business results.







